A voltage converter is an electric power converter that changes the voltage of an electrical power source. On this page, I am going to talk about the DC-DC converter. In the DC-DC converter, there are 3 types.
1. Step-down(Buck) converter: Where the output voltage of the converter is lower than the input voltage.
In a buck converter, there are two types of modes. Continuous conduction mode(CCM) and Discontinuous conduction mode(DCM). During CCM(Mode 1), while switch S is on, the voltage of the load is conducted as V_s. During DCM(Mode 2), while switch S is off, any current doesn't flow.
V_a=F(t_on, f_s) is a linear function. t_on is the on pulse width. Controlling t_on is known as PWM control. f_s is the switching frequency.
Low current ripple(by adding inductor)
This is a buck converter which provides a low current ripple by adding an inductor on load.
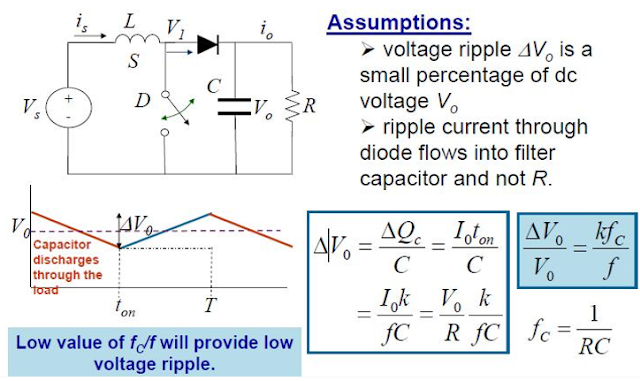
Low voltage ripple(by adding capacitor)
This is a buck converter which provides low voltage ripple by adding inductor and capacitor on load
2. Step-up(Boost) converter: Where the output voltage of the converter is higher than the input voltage.
In Boost converter, there are two types of modes. Continuous conduction mode(CCM) and Discontinuous conduction mode(DCM). During CCM(Mode 1), while switch S is on, the voltage of the load is conducted as V_s by capacitor containing the charge. During DCM(Mode 2), while switch S is off, the inductor releases voltage in this mode.
Low Current Ripple
Low Voltage Ripple
3. Step-down/step-up (Buck-Boost) converter: It can be used in any case.
Comparison of voltage ratio
This graph indicates voltage ratio by duty ratio in each converter. Notice that only the buck converter shows a linear relationship between the control (duty ratio) and output voltage. The buck-boost can reduce or increase the voltage ratio with unit gain for a duty ratio of 50%.










댓글
댓글 쓰기